Confidential information such as contracts, financial reports, employee or customer data is often exchanged via email. These emails are mostly not encrypted. With Information Rights Management (IRM), encrypted emails can be sent and received between people inside and outside your organization. Sent emails and their replies are encrypted automatically with transport rules or manually from Exchange Online email client (Outlook and Outlook.com).
Information Rights Management (IRM) ensures that only intended recipients can open and read the message. It is also possible to prevent emails from being forwarded, printed or parts of them copied. Message encryption works with Outlook, Outlook.com, Gmail and many other popular email services.
Prerequisites and Licensing
Information Rights Management (IRM) requires licensing of Azure Information Protection (AIP).
For example, Azure Information Protection (AIP) is included in the following license packages:
- Microsoft 365 E3 or E5
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium
- Office 365 E3 or E5
or can be licensed as a stand-alone SKU:
- Azure Information Protection P1
This listing is not complete.
An overview of Microsoft 365 license packages with their features can be found at https://m365maps.com.
Encryption method
Microsoft offers 3 different encryption methods for emails.
This tutorial describes the configuration of Information Rights Management (IRM).
Office 365 Message Encryption (OME)
Office 365 Message Encrytpion is a service based on Azure Rights Management (Azure RMS). Emails are sent and received encrypted inside or outside the organization.
Messages are encrypted via transport rules in Exchange Online. When a user sends a message that matches a rule, encryption is automatically applied. To view encrypted messages, recipients can either retrieve a unique identifier, sign in with a Microsoft account, or sign in with a business or school account associated with Office 365. If an encrypted email is answered, it will be sent encrypted as well. You do not need a Microsoft 365 subscription to view encrypted messages or send encrypted replies.
Information Rights Management (IRM)
IRM is an encryption solution that can also apply usage restrictions to emails. This solution prevents confidential information from being printed, forwarded or copied by unauthorized persons.
IRM features in Microsoft 365 use Azure Rights Management (Azure RMS).
Secure/Multipurpose internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME)
S/MIME is a certificate-based encryption solution that both encrypts and digitally signs messages. Message encryption can ensure that only the intended recipient can open and read the message. With the help of a digital signature, the recipient can verify the identity of the sender.
More information about the encryption methods provided by Microsoft can be found at Email encryption in Microsoft 365 – Microsoft Purview (compliance) | Microsoft Learn.
Configuration
Prerequisites for Information Rights Management (IRM)
Information Rights Management (IRM) requires Azure Information Protection. This feature is activated with an appropriate license. PowerShell can be used to check if the feature is active.
1 2 3 4 | Install-Module -Name ExchangeOnlineManagement Import-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement Connect-ExchangeOnline -ShowProgress $true Get-IRMConfiguration |
The value for “AzureRMSLicensingEnabled” is set to “True”
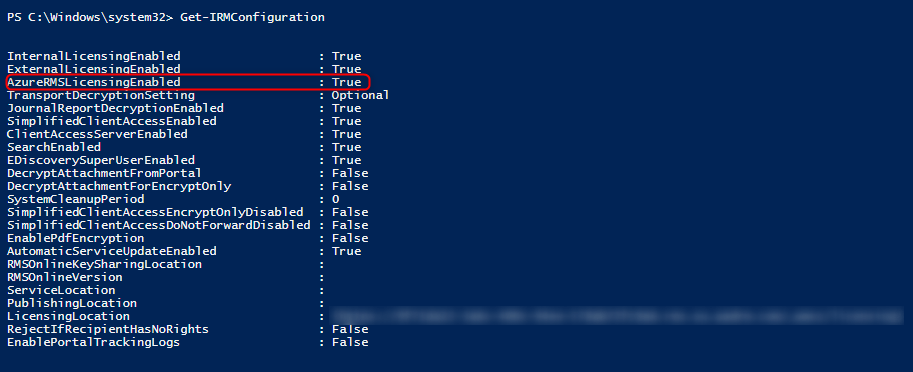
If “AzureRMSLicensingEnabled” is not set to “True” and the organization is licensed correctly, the following PowerShell will enable the feature.
1 | Set-IRMConfiguration -AzureRMSLicensingEnabled 1 |
Testing of Rights Management Services (RMS)
After ensuring that “AzureRMSLicensingEnabled” is enabled, the Rights Management Services (RMS) can now be checked.
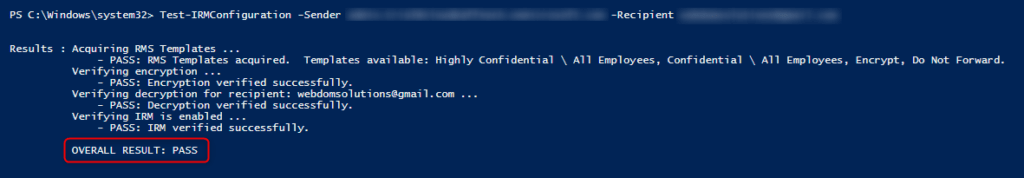
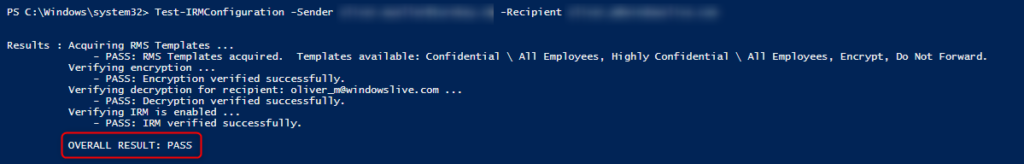
The check is done with the following PowerShell cmdlet (replace sender and email address)
1 | Test-IRMConfiguration -Sender sender@tenant.onmicrosoft.com -Recipient recipient@tenant.onmicrosoft.com |
If “OVERALL RESULT: PASS” is shown, the Rights Management Services (RMS) is configured correctly.
Use encryption
Encrypt email automatically (create transport rules)
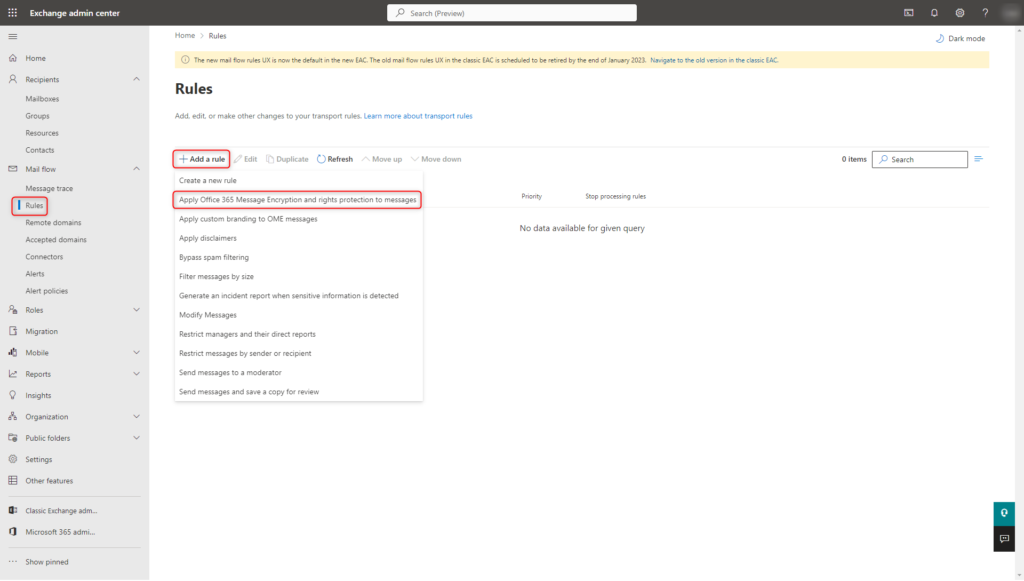
Transport rules are used to specify which messages are automatically encrypted by Exchange Online when they are sent. Transport rules are configured in the Exchange Online Admin Center.
Exchange Online Admin Center > “Mail Flow” > “Rules” > “Apply Office 365 Message Encryption and rights protection to messages…”
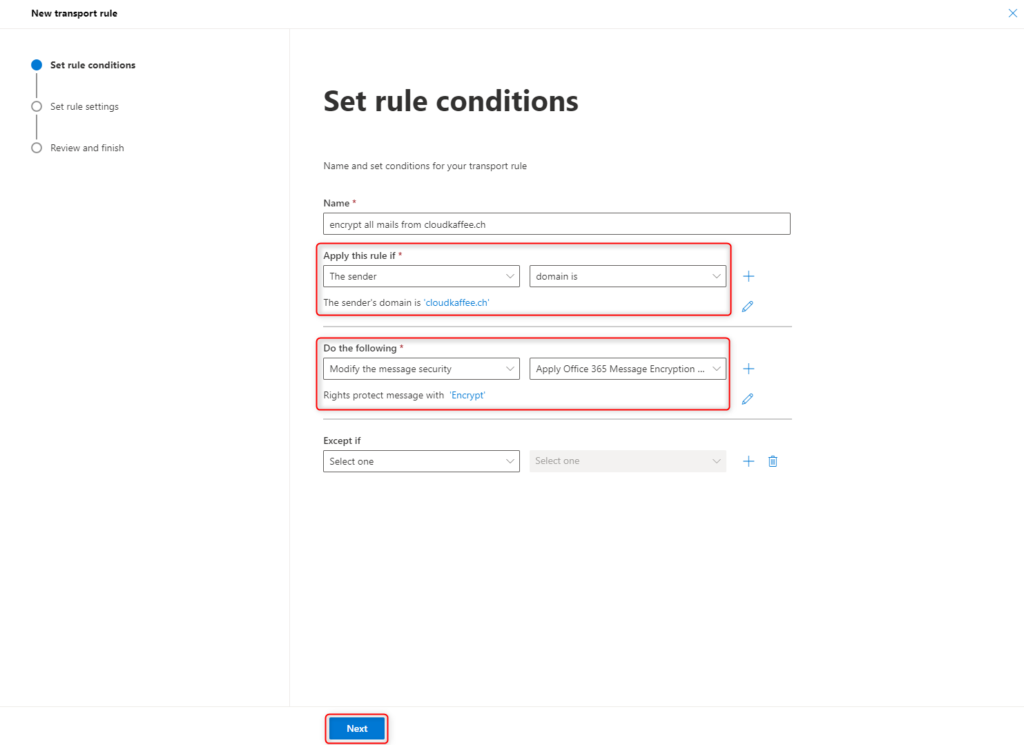
In the newly opened “New Rule” dialog, the conditions for the encryption of messages can now be specified. In this example, all messages from the domain “cloudkaffee.ch” are encrypted.
The rule should always be applied.
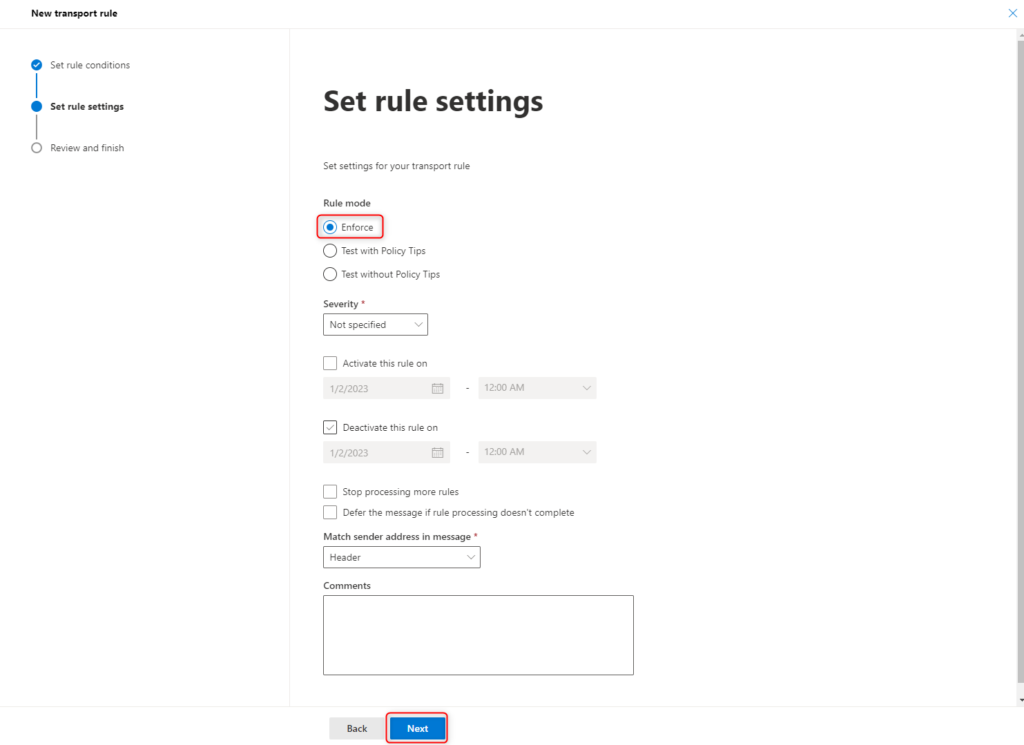
Check the settings again and confirm them by clicking Finish.
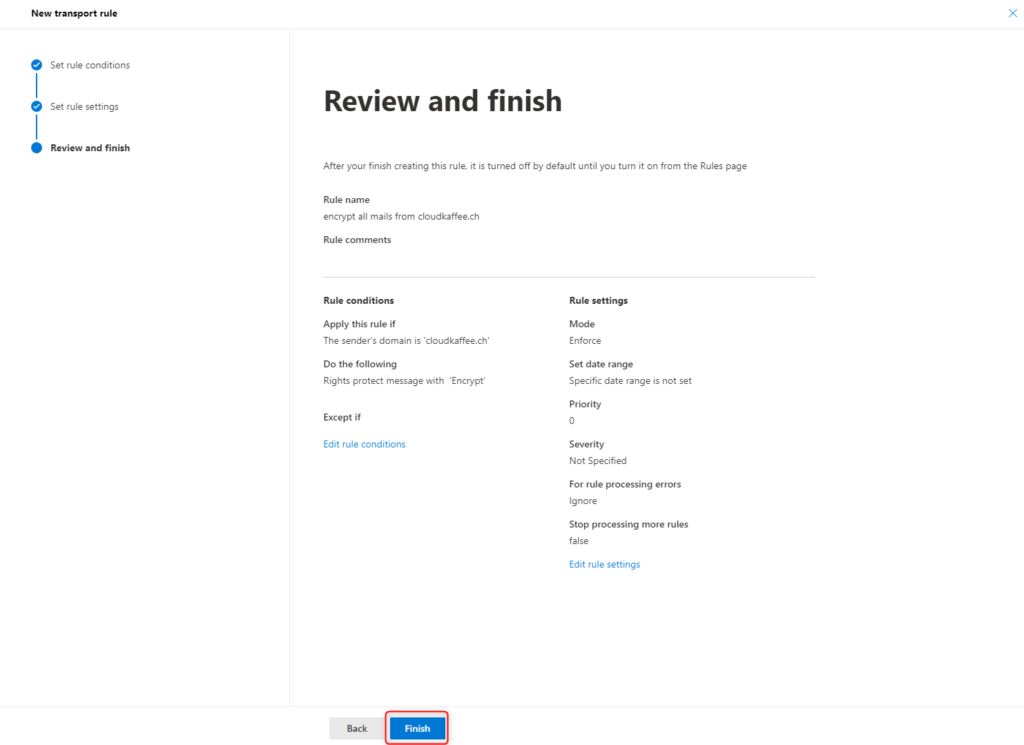
The new policy is created successfull.
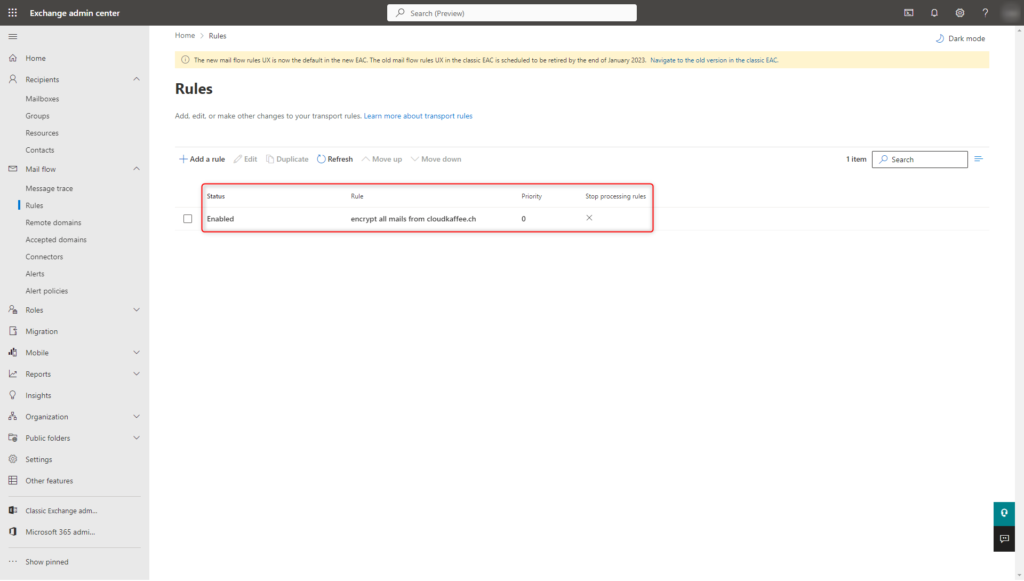
The status of the new policy must be Enabled.
Encrypt email manually
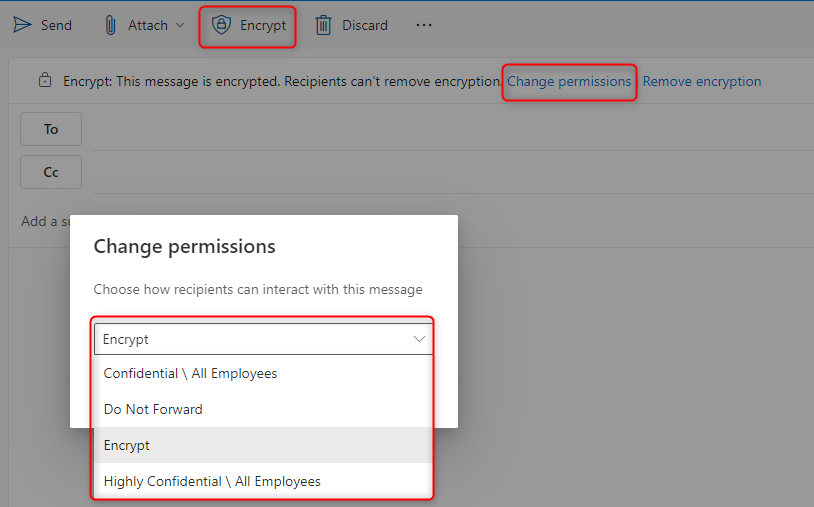
When creating emails in Outlook or Outlook.com, you can manually select different options to protect the message:
Encrypt-only
The email is encrypted and the recipient must authenticate.
Do not forward
The email is encrypted and the recipient must authenticate.
In addition, recipients cannot forward, print or copy parts of the email.
Confidential\ All Employees
The email is encrypted and the recipient must authenticate.
In addition, recipients can only read, reply to or forward the email within the organisation.
High Confidential \ All Employees
The email is encrypted and the recipient must authenticate.
The email can only be read within the organisation.
In addition, recipients cannot reply, forward, print or copy parts of the email. External recipients cannot view the email.

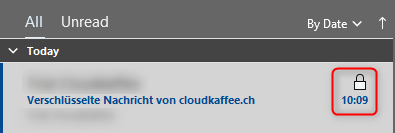
Access to encrypted emails
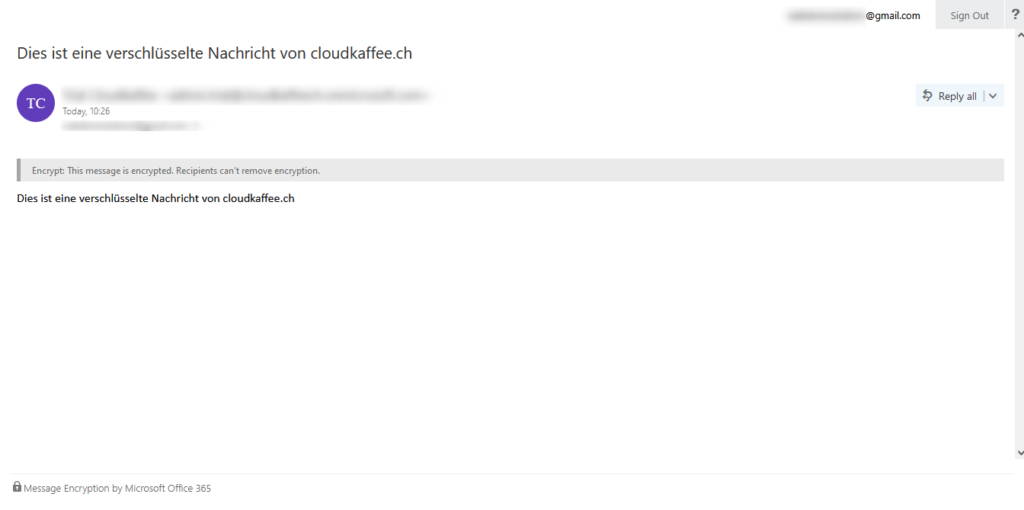
The recipient recognizes the encrypted email by the “lock” symbol.
In order to open the received email, it requires one of the following authentications:
- Business or school account (Microsoft 365 account)
- One-time passcode (numerical code)
- Microsoft account (Hotmail etc.)
Decrypt email automatically
If the recipient already uses a business, school or Microsoft account in connection with Outlook or Outlook.com, the message is automatically decrypted and displayed without any further interaction.
If the recipient replies to this email, it is also encrypted.
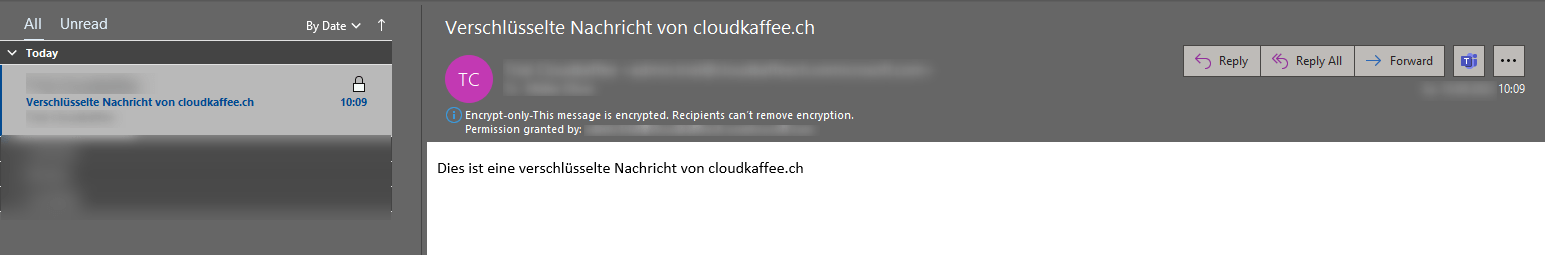
Decrypt email manually
If the decryption of the email cannot be performed automatically, either because no business, school or Microsoft account is sign in on the client or because no supported mail service for this is used, the following message appears in the recipient’s mailbox.
By clicking on “Read the message” the authentication can be performed manually.

The following options are now available:
- Manual signin with an existing business, school or Microsoft account
- One-time passcode, the numerical code is sent by email and is valid for 15 minutes

Signin with one-time passcode
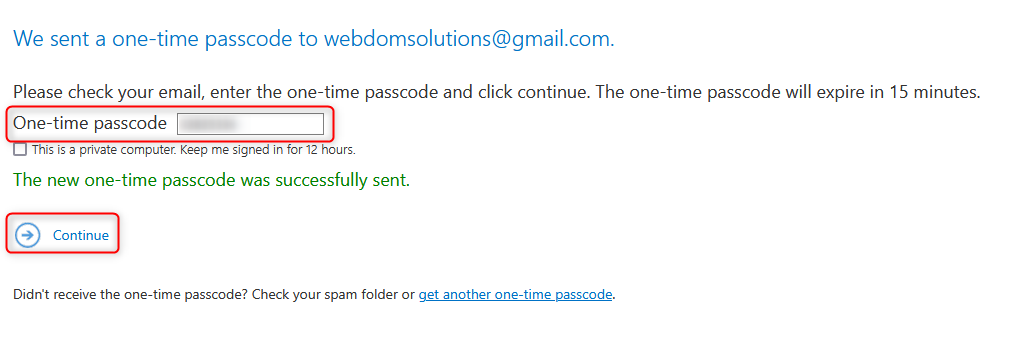
The email is now shown decrypted in the browser.
If the recipient replies to this email, it is also encrypted.
Troubleshooting
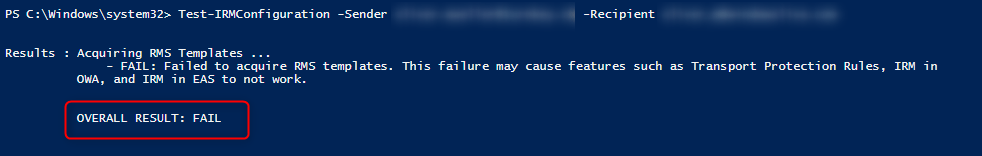
IRM-Configuration OVERALL RESULT: FAIL
The Right Management Service (RMS) check fails with the message “OVERALL RESULT: FAIL”.
1 | Test-IRMConfiguration -Sender sender@tenant.onmicrosoft.com -Recipient recipient@tenant.onmicrosoft.com |
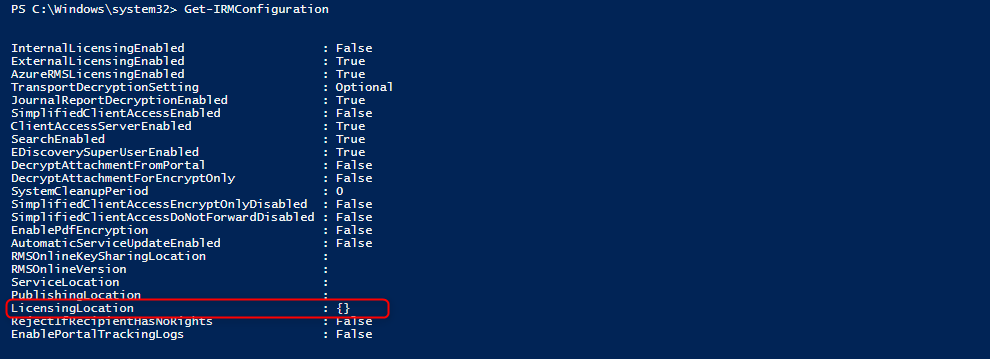
The reason for the unsuccessful test is that the value for “LicensingLocation” is not set.
1 | Get-IRMConfiguration |
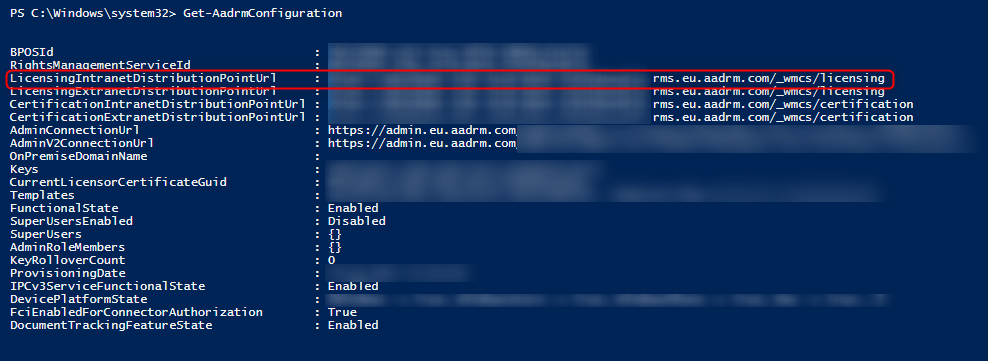
The correct value for “LicensingLocation” can be retrieved in AzureAD Rights Management Services. Copy the necessary value of “LicensingIntranetDistributionPointUrl” to the clipboard.
1 2 3 | Install-Module AipService Connect-AipService Get-AadrmConfiguration |
The value from “LicensingIntranetDistributionPointUrl” can now be stored at “LicensingLocation” with the following PowerShell cmdlet.
1 2 | Set-IRMConfiguration -LicensingLocation "Value from Clipboard" Set-IRMConfiguration -InternalLicensingEnabled $true |

The value for “LicensingLocation” is now set.
1 | Get-IRMConfiguration |

After waiting up to 24 hours, the Right Management Service (RMS) can be checked successfully.
1 | Test-IRMConfiguration -Sender sender@tenant.onmicrosoft.com -Recipient recipient@tenant.onmicrosoft.com |
No RMS templates available in the organization
Thanks for pointing out this challenge Harald Bättig.
When creating the Exchange transport rule for automatic encryption of emails, there are no RMS templates available.
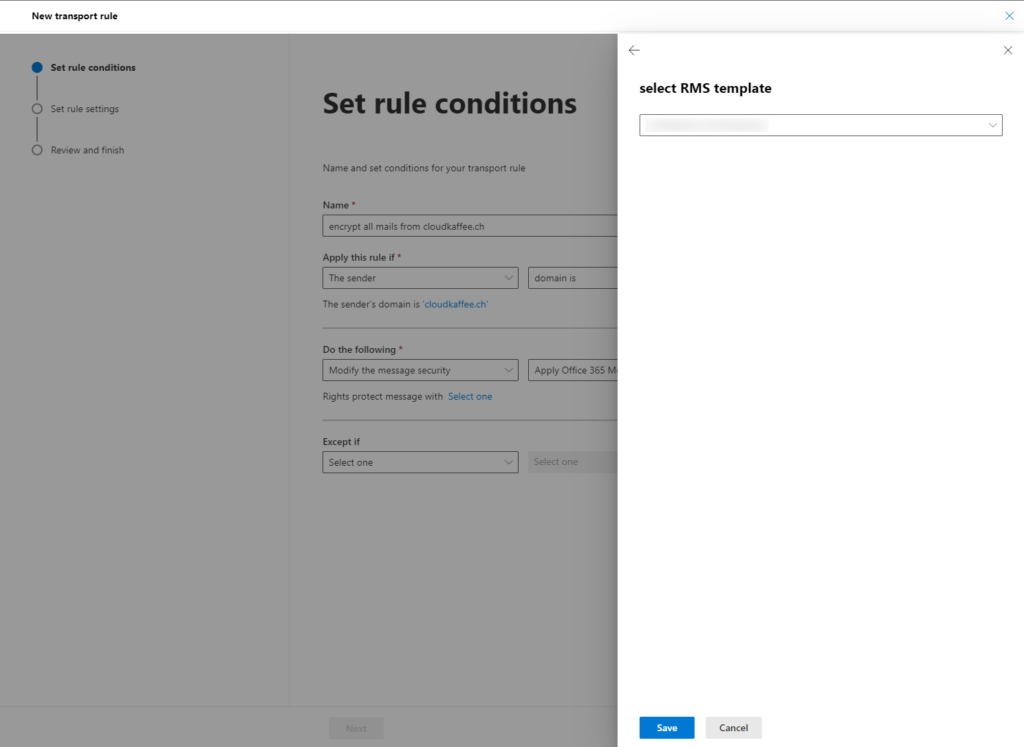
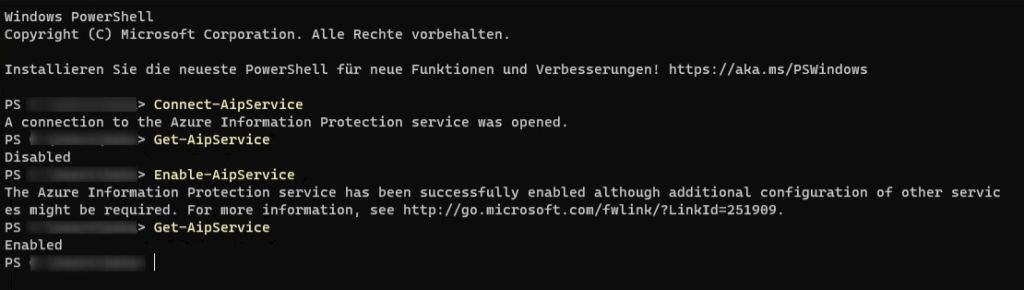
The reason for this is that the Azure Information Protection (AIP) service is not active. You can check this with the following PowerShell cmdlet:
1 2 | Connect-AipService Get-AipService |
If the value for AipService is shown as Disabled, run the following PowerShell cmdlet to enable it.
1 | Enable-AipService |
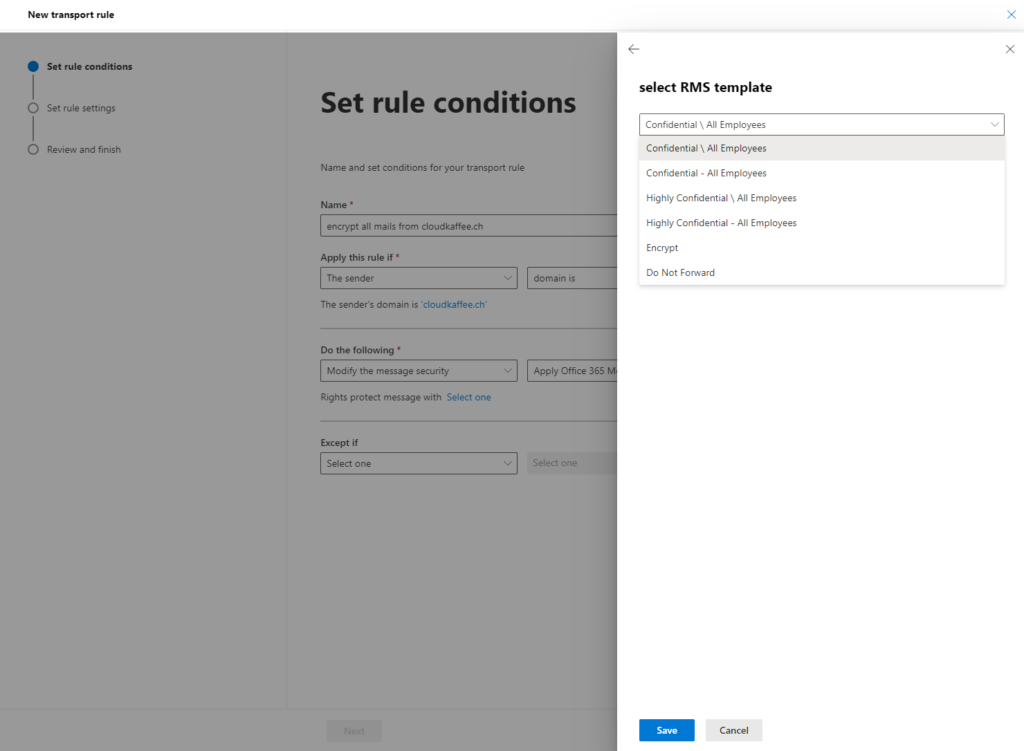
After a waiting up to 60 minutes, the RMS templates are created and can be selected in the Exchange transport rule.
Follow me on LinkedIn and get informed about my latest posts.
